
Author: Emanuele De Lucia
Pubblication date: 17/09/2021
This report presents an overview about Dharma/Crysis ransomware. This piece of malware is often observed as late-stage payload in attacks against internet-facing systems, such as RDP.
The initial intrusions usually take place via existing vulnerabilities or stolen legitimate credentials. C25 Intelligence finally reports from where Dharma variants have been operated during 2020 and how to defend against this threat.
Dharma, a family of ransomware first spotted in 2016, is a malicious program that encrypts a victim’s files and takes as hostage the data on demand for the ransom payment to restore the data back. It belongs to a fairly widespread ransomware family that has been successful over time, especially due to the many variants related to it and the fact that it has often represented the basis for R-a-a-S (Ransomware-as-a-Service) programs.
The R-a-a-S Dharma model is often adopted by novice cybercriminals looking for something immediate and easy to use. Indeed, threat actors using this R-a-a-S are equipped with a matrix of predefined scripts and tools that require little skill to work. This toolset greatly increases the attractiveness of this solution for those at the entry-level in ransomware operations.
Today we can define Dharma as the basis for Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS); it has become one of the most profitable and easy to deploy ransomware especially for those who are new to ransomware attacks.
Dharma was operated by a cyber gang who managed to remain mostly in the shadows to this day. At the beginning CrySiS (the originator of Dharma) was offered as a R-a-a-S (Ransomware-as-a-Service) meaning that “clients” could use it if they purchased a license from the coders. This means that those who purchase the malware carry out the actual attacks rather than original creators.
After the master decryption key leak of CrySiS in November 2016, its R-a-a-S model has been relaunched under the name of Dharma two weeks later..
Since then, the malware developers have released a constant flow of new Dharma variants utilizing many differently named extensions. The FBI has ranked Dharma the second most lucrative ransomware operation in recent years.
C25 Intelligence traces the origin of the first CrySiS variants to Ukraine, a country in which it places its original developers with high confidence.
Dharma, instead, is not centrally administrated and its variants come from different sources. In 2020, for example, C25 Intelligence observed variants to be controlled from the following cities/Countries:
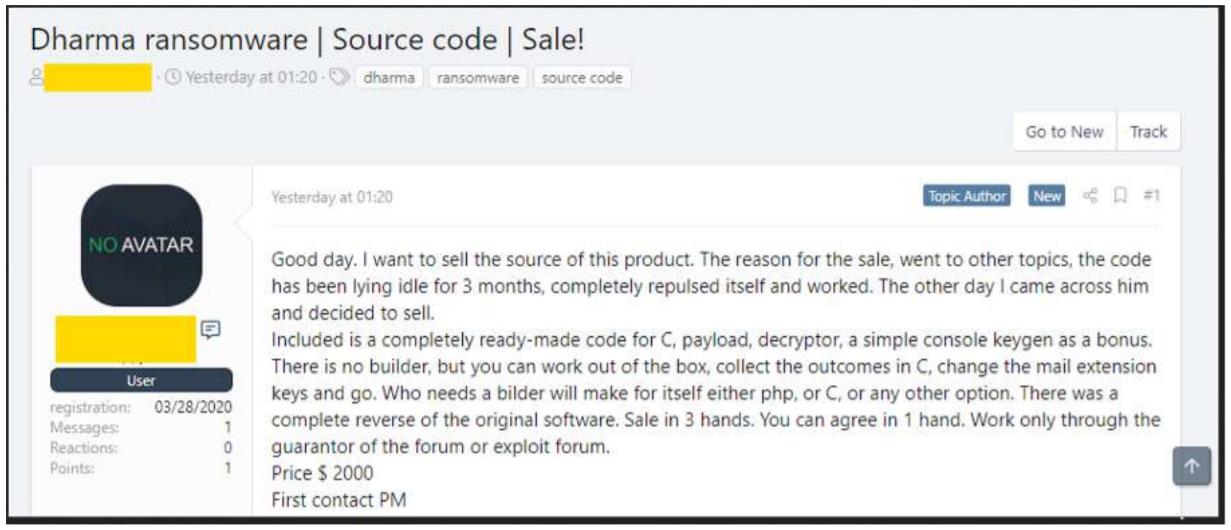
In March 2020 the source code for ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) strain of Dharma was observed being put for sale on a top-tier deep web forum for 2,000 USD.
Victimology of Dharma ransomware does not differ much from distinct Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) gangs, Dharma ransomware affiliates do not appear to discriminate among industries.
Victims have been identified in the following sectors:
These intrusions have shown consistent techniques that include gaining initial access over Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), brute forcing or password spraying, using publicly available utilities to attempt to identify and uninstall security software, harvesting credentials and mapping network shares.
Cluster25 managed to map all the infection chain used by Dharma Ransomware affiliates. Dharma Ransomware targets Windows systems, and this family primarily targets businesses. It uses several methods of distribution:
Dharma does not stop the affected system from working properly after the encryption is finished, but every time a file is added to the targeted directories, it will be encrypted unless the Dharma Ransomware infection is removed.
Once the Ransomware has completed the encryption routing it drops a ransomware note on the desktop of the victim providing usually 2 email addresses which the victim can use to contact the threat actor in order to pay the ransom.
Dharma encrypts user data with AES-256 (CBC mode) or DES + RSA. The file decryption key, along with random bytes, is encrypted using the RSA-1024 algorithm and stored at the end of the encrypted file.
On other malicious sample that we have analyzed some ransomware notes contain only one email address.
The ransomware can be different in relation to variants and affiliates. Some of them will not have a ransom note. During the outbreak of coronavirus pandemic, we have seen that also Dharma Ransomware took part into this cybercrime ecosystem pushing their malicious payload into tricking the victims to download harmless looking installers for various legitimate applications to watch for Coronavirus infection
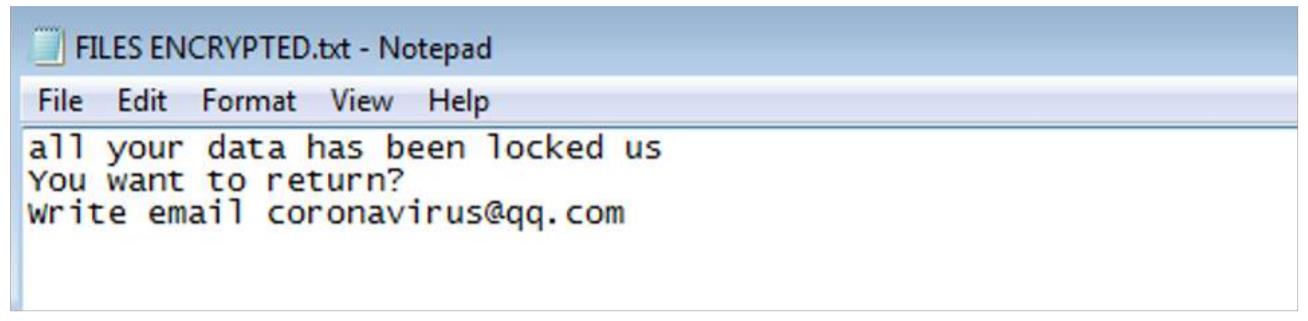
Another example of the ransomware note that the victims see on their desktop once they are infected/ encrypted are shown below from .lol and .biden variants:
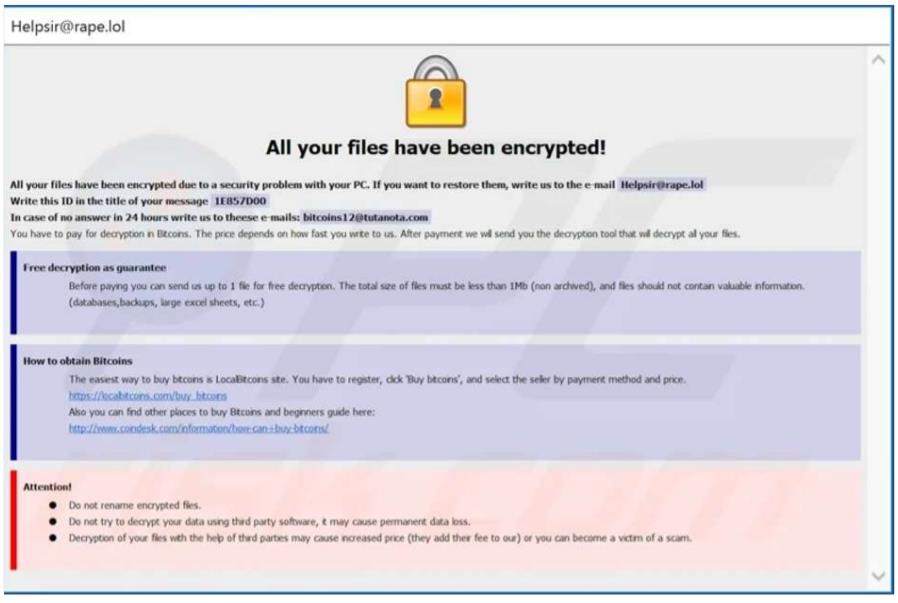
ransom note example of .lol
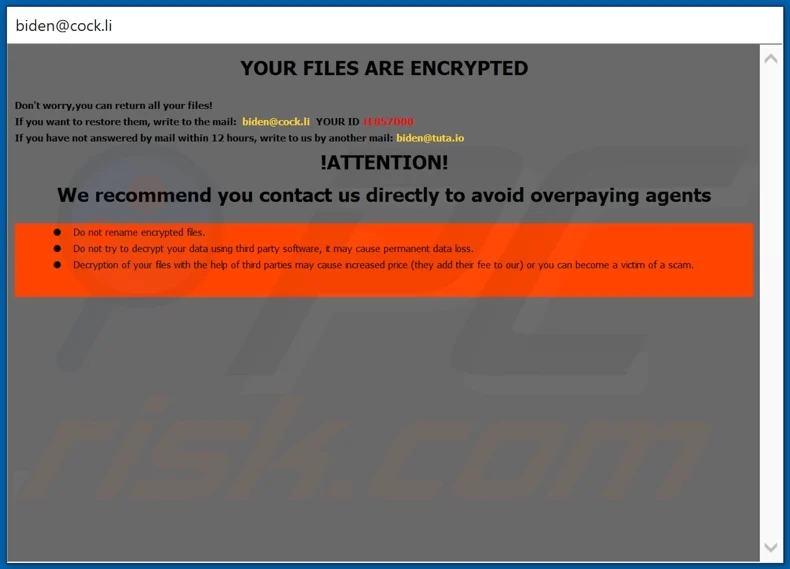
ransom note example of .biden
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.