
Privacy, privacy, privacy, … privacy comes first.
How many times have we heard this sentence?
Yes, because we talk a lot about this topic, we talk about it at work, we talk about it at school, we talk about it at the bar because it is a concept that in a democratic world should be a right, but in fact, in the era of digital, social, mobile phones as a “prosthesis” of our body, it could be a utopia today.
But I don’t want to jump to any would not like to draw conclusions, today I would like to talk about this topic in a different way, telling you a story, in no uncertain terms, I will tell you the story of “mass surveillance”, leaving the necessary final conclusions to you.
But I assure you that – for many – it will not be easy to read all this.
You are ready? Let’s start.

After the Second World War. after the signing of the Atlantic Charter in 1941, an agreement was secretly signed between Great Britain and the United States of America (UKUSA agreement) to collect information through activities of SIGINT (SIGnal INTelligence which deals with the interception of communications between people or through electronic signals ).
In the following years, Canada, Australia and New Zealand also took part in this agreement, giving rise to what is now called Five Eyes (five eyes) or a joint cooperation treaty in the field of signal intelligence, which gave rise to the Echelon network, created between the 60s and 2000s.
This network consisted of a constellation of spy satellites put into orbit by the NSA, as well as using several submarine cables. In fact, the system intercepted private and public subjects, without any distinction and, given the large amount of data collected, there were various data processing centers in the world such as in the USA, Great Britain and Australia.

Echelon controlled all terrestrial radio transmissions and communications over the Internet, particularly the sorting of email messages. Over the years, numerous questions have been raised with the European Parliament on Echelon (such as that of 11 July 2001 by Gerhard Schmid), and its use has also been suspected for illegal purposes.
But after the advent of the Internet as a mass phenomenon, everything changed …
for the worse.
In 1978 the United States of America issued the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act, an amendment that provides specific procedures for physical and electronic surveillance and the collection of data on foreign people.

The most contested section is the 702 (renewed several times, the last time in 2018 by Donald Trump) which provides and grants immunity to telecommunications companies for active cooperation with the authorities and we are talking about the whole ecosystem of services and internet social networks that we use.
But after 9/11, Bush initiated the “Terrorist Surveillance Program,” an electronic surveillance program run by the National Security Agency (NSA). This program allowed the United States to secretly spy on billions of phone calls made by millions of US citizens over the course of decades.

All this was well understood with the DataGate scandal of 2013, when Edwared Snowden unearthed a series of classified documents and programs for the aggregation and interception of Internet traffic, such as PRISM, which collected electronic traffic from 100 American companies. such as chat, e-mail, skype traffic, etc … allowing the execution of queries on metadata guaranteeing US intelligence indiscriminate access to users’ private communications.
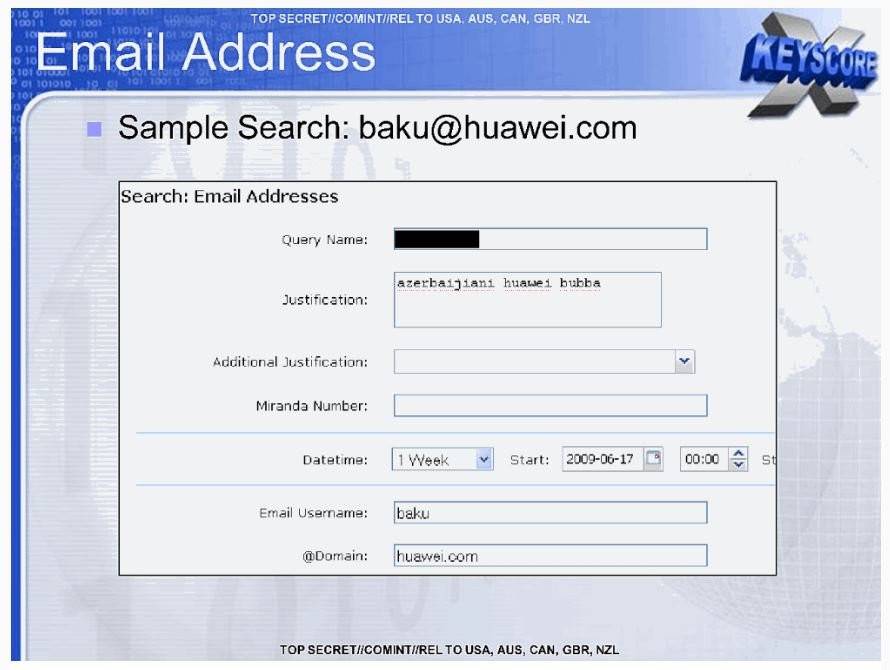
After PRISM we were told about XKeyScore, the User Interface that allowed almost unlimited surveillance of anyone anywhere in the world, and then Tempora of the British Government Communications Headquarters which carried out the interception of internet traffic across the Atlantic undersea ridges.
In fact, the NSA collected millions of video chats, instant messages and emails, under FISA, from companies like Facebook, AT&T and Google, Microsoft, Apple, to name a few.
On May 26, 2017, the 30 major American electronic services companies wrote to Bob Goodlatte, a Republican member of the House, deputy to oversee the administration of justice in federal courts, calling for the termination of section 702 of the FISA but without success.

The signatory companies were: Adobe, Airbnb, Amazon, Atlassian, Automattic, Cisco Systems, Cloudflare, Computer & Communications Industry Association, Consumer Action, cPanel, Data Foundry, Dropbox, Engine, Evernote, Facebook, Golden Frog, Google, i2Coalition, Internet Association, LinkedIn, Lyft, Microsoft, Mozilla, Pinterest, Rapid7, Reddit, Snap, Sonic, Twitter, Uber, Yahoo.
The law also allows the FBI to search the NSA’s database without a warrant, constituting what critics like Democratic Senator Ron Wyden call a backdoor to the Fourth Amendment.
But then we witnessed in 2017 the WikiLeks Vault7 scandal which brought to attention how the American Central Intelligence Agency, precisely the CIA, could sneak into any Smartphone, computer or smart TV through Weeping Angel, AfterMidnight, Pandemic, NightSkies , Dark Matter and many more.
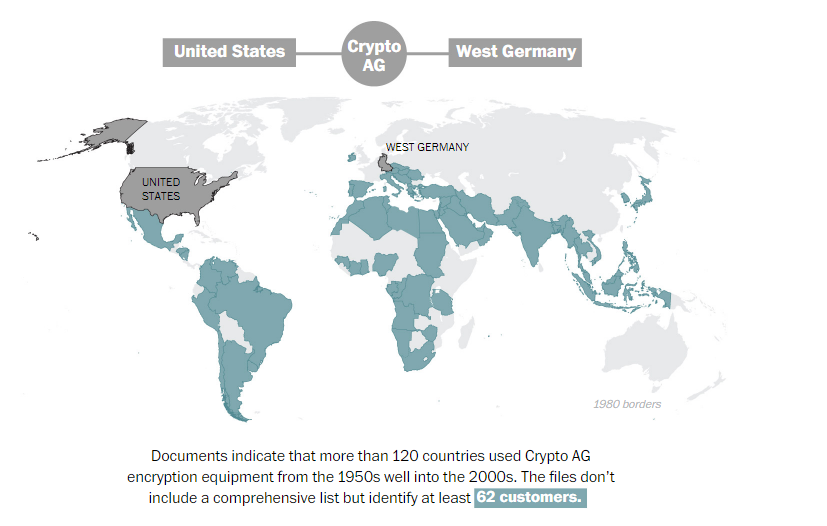
And more recently, in early 2020, the Crypto AG scandal, which brought to the attention that for 50 years America spied on classified and encrypted communications from over 120 countries, including Italy, the Vatican and China as the Cryto AG, secretly controlled by the CIA, allowed access to over 5 billion cellphone calls worldwide, control 3 million computers in China and implant Trojans on more than 3,600 Chinese websites.
But apart from the intelligences we have the private market of zeroday (we talked about it in a previous video), the resale of exploits in darknets, the National State Actors, cybercrime, companies that resell interception systems to individuals or government bodies ( let’s remember the Italian Hacking Team and RCS Galileo), the market of fake apps and geolocation, advertising, and much more to deeply undermine the concept of privacy.
In short, just pay and you will get everything.
The great Bruce Shneier said at an RSA conference a few years ago
the business model of the internet is surveillance
Now, if you’ve come to the end of this article, rethink the concept of privacy draw your own conclusions.
Follow us on Google News to receive daily updates on cybersecurity. Contact us if you would like to report news, insights or content for publication.
